Treatment Specialties
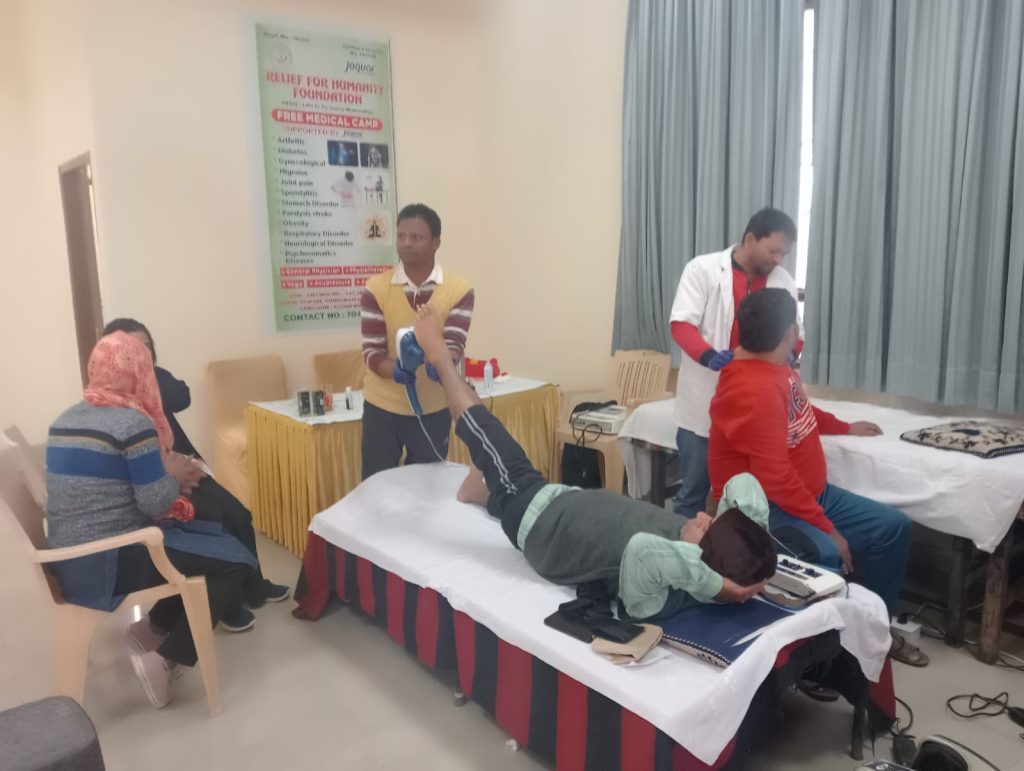
1. PHYSIOTHERAPY
Physiotherapy promotes physical health through exercises, manual therapy, and education. It aids in recovery from injuries, reduces pain, and improves movement and function. Techniques include stretching, strengthening, and postural training to enhance mobility and prevent future issues. Physiotherapists work with individuals of all ages to address musculoskeletal, neurological, and cardiovascular conditions. Personalized treatment plans focus on restoring optimal function and enhancing overall quality of life.
2. Hijama Cupping Therapy

Hijama, or cupping therapy, is a traditional practice that involves placing cups on the skin to create suction, drawing blood to the surface. This technique is believed to help with pain relief, inflammation reduction, and improved circulation. The therapy can be dry, where cups are simply placed on the skin, or wet, where small incisions are made to release blood and toxins. Often used for conditions like back pain, migraines, and muscle tension, hijama is thought to balance energy flow and promote healing. While many report benefits, it’s essential to consult a qualified practitioner and consider it as a complementary treatment alongside conventional medical care. Safety, hygiene, and proper technique are crucial to maximize benefits and minimize risks.
3.Accupressure
Acupressure is an ancient therapeutic practice rooted in Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM), which involves applying pressure to specific points on the body to promote healing and balance. It operates on the principle that energy, or “qi,” flows through meridians or channels in the body. By targeting specific acupoints, acupressure aims to release blockages and restore the smooth flow of energy. This practice can help alleviate a variety of conditions, including stress, headaches, back pain, and digestive issues. It is non-invasive and uses fingers, thumbs, or hands to apply pressure, making it accessible for self-care or professional treatment. Regular acupressure sessions can enhance overall well-being, improve circulation, and support the body’s natural healing processes. While it is generally safe, it’s important to consult with a healthcare professional, especially if you have underlying health conditions or are pregnant.
4.Accupunture

Acupuncture is a traditional Chinese medicine technique that involves inserting thin needles into specific points on the body to stimulate energy flow, or “qi,” along meridians. The goal is to restore balance and promote natural healing. Used to address a range of conditions, including chronic pain, stress, and digestive issues, acupuncture aims to alleviate symptoms by targeting points that correspond to various bodily systems. The procedure is typically well-tolerated, with minimal discomfort. Sessions usually last 20-60 minutes and may involve multiple treatments for optimal results. While acupuncture is considered safe, it’s crucial to seek treatment from a licensed and experienced practitioner. It is often used alongside conventional medicine to enhance overall health and well-being.
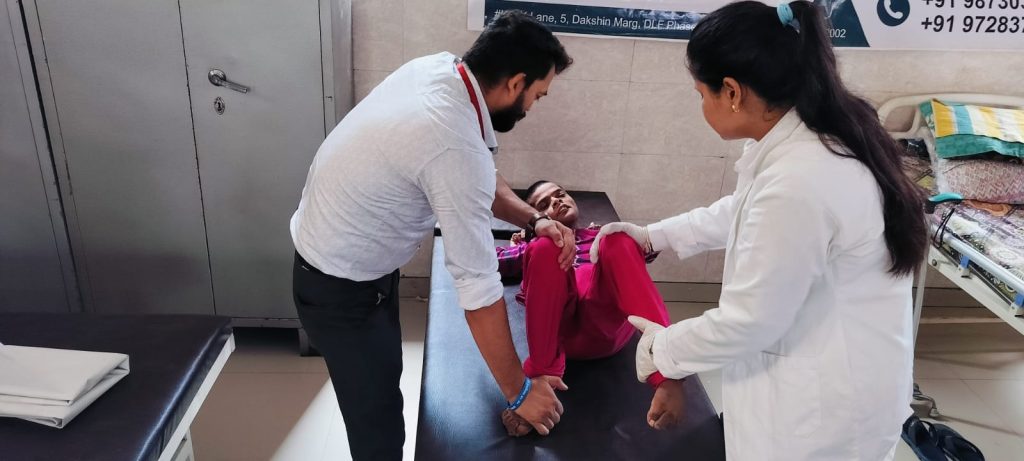
5. Back Pain & Stiffness
Back pain and stiffness are common issues that can stem from various causes, including poor posture, muscle strain, or underlying conditions like herniated discs or arthritis. These symptoms can disrupt daily activities and affect quality of life. Effective management typically involves a combination of strategies such as physical therapy, which strengthens and stretches muscles; ergonomic adjustments to improve posture; and pain relief techniques like heat therapy or medications. Regular exercise, including low-impact activities like swimming or walking, can also help alleviate discomfort and prevent future issues. Additionally, maintaining a healthy weight and practicing proper lifting techniques can reduce strain on the back. If symptoms persist or worsen, consulting a healthcare professional for a thorough evaluation and personalized treatment plan is essential.

6. Paralysis
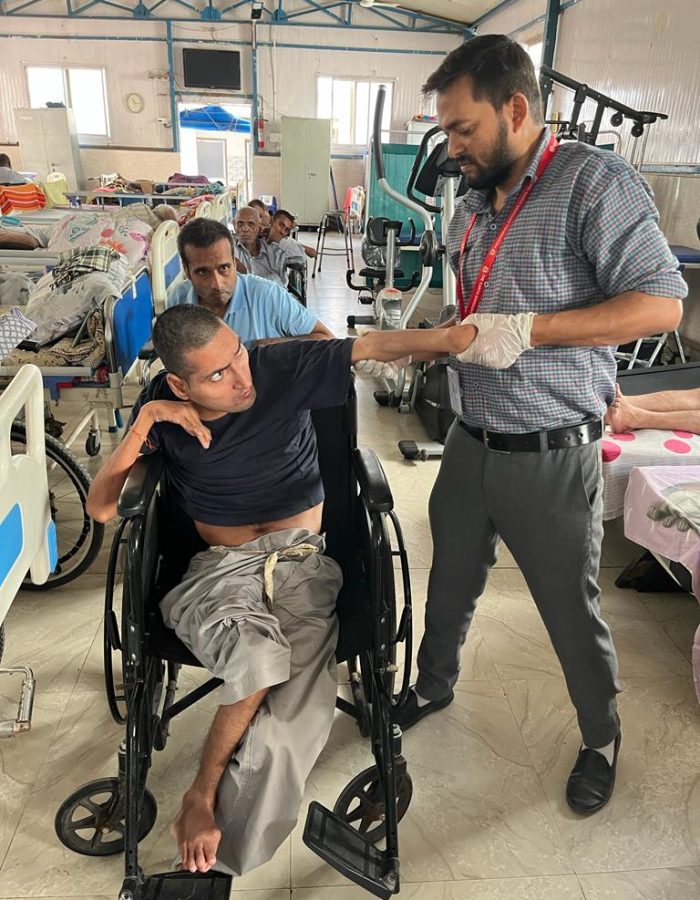
Paralysis is the loss of muscle function in part of the body, often caused by damage to the nervous system. It can result from strokes, spinal cord injuries, traumatic brain injuries, or conditions such as multiple sclerosis or cerebral palsy. Paralysis may be partial (paresis) or complete and can affect one side of the body (hemiplegia), the lower half (paraplegia), or all four limbs (quadriplegia). Symptoms include muscle weakness, loss of sensation, and impaired movement. Treatment varies depending on the cause and severity and often involves physical therapy to maintain muscle strength, prevent contractures, and improve mobility. Medications and surgical interventions may also be necessary to address underlying conditions. Adaptive devices and assistive technologies can enhance daily functioning and independence. Early diagnosis and a comprehensive rehabilitation plan are crucial for optimizing recovery and improving quality of life.
7. Muscular Pain
Muscular pain, or myalgia, refers to discomfort or soreness in the muscles, often caused by strain, overuse, or injury. It can also result from conditions like fibromyalgia or muscle infections. Common causes include intense physical activity, poor posture, or repetitive motions. Symptoms range from mild stiffness to severe, debilitating pain and may be accompanied by muscle cramps or spasms. Management typically involves rest, ice or heat therapy, and over-the-counter pain relievers such as NSAIDs. Stretching and strengthening exercises, guided by a physical therapist, can aid in recovery and prevent future issues. Maintaining proper posture and ergonomics during activities is essential to avoid muscle strain. If muscular pain persists or is associated with other symptoms like swelling, weakness, or fever, seeking medical attention is important to rule out more serious conditions and develop an appropriate treatment plan.

8. Arthritis

Arthritis is a general term for conditions that cause inflammation and pain in the joints. The two most common types are osteoarthritis (OA) and rheumatoid arthritis (RA). OA occurs due to the wear and tear of cartilage over time, leading to pain and stiffness, particularly in weight-bearing joints like the knees and hips. RA is an autoimmune disorder where the immune system attacks the synovial lining of the joints, causing inflammation, swelling, and eventual joint damage. Symptoms of arthritis include joint pain, stiffness, swelling, and decreased range of motion. Management strategies involve medication to reduce pain and inflammation, physical therapy to improve joint function, and lifestyle changes such as weight management and exercise. In severe cases, surgical options like joint replacement may be considered. Early diagnosis and a comprehensive treatment plan are crucial to managing symptoms and maintaining quality of life.
